Having an enlarged scrotum? A scrotal swelling can be painful and cause a lot of discomfort. This article provides an insight into the causes of scrotal swelling such as testicular cancer and scrotal edema, the symptoms and treatment. Read through to find out more about the condition.
Scrotal swelling is an enlargement of the scrotal sac which might be caused by an injury or an underlying medical condition, other causes include accumulation of fluid, scrotal edema, inflammation or an abnormal growth within the scrotum. Symptoms vary depending on the causes of the scrotal swelling
What does a swollen testicle mean?
A swollen testicle basically means an abnormal enlargement of the testicles. It is known as ORCHITIS, it is an inflammation of one or both testicles in men, commonly caused by an infection. It can also result from the spread of bacterial through the blood from other body parts. It can also be a progression of epididymitis, an infection of the urethra (the tube that carries semen out of the testicles) this is called epididymo-orchitis. This mostly leads to scrotal swelling.
The main causes of swollen testicle are virus and bacteria. Bacteria that causes STDs such as gonorrhea, syphilis and chlamydia can also cause swollen testicles (orchitis). Most cases of swollen testicles as a result of bacteria requires antibiotics right away. If you suspect that you have the disease, or you notice redness, swelling, pain or scrotal swelling see your health care provider immediately.
The virus that causes mumps can also cause scrotal swelling. A bigger percentage of boys with mumps develops swollen testicles. See you doctor as soon as you notice the above symptoms.
Scrotal swelling pictures
Pictures are to help you identify your symptoms. Below here we have inserted an image to help you understand vividly the cause and symptom of enlarged scrotum. We also have more photos throughout the post for illustration and better insight on this condition.
Scrotal swelling symptoms
Symptoms of scrotal swelling vary depending on the causes of the enlargement and inflammation. The most common symptoms would include, but not limited to:
- Enlargement of the scrotal sac.
- Lump in the testicles
- Pain in the testicles and scrotum
- A sudden, severe pain in one of your testicles.
- nausea
- Abdominal (tummy) pain.
You need to see your doctor as soon as you notice the above symptoms.
Scrotal swelling causes
Causes of scrotal swelling vary from one person to another. The following are the main causes of scrotal swelling.
1.Scrotal edema
Edema is the swelling caused by fluid retention- excess fluid is trapped in the body’s tissues. Scrotal edema occurs when body fluid are trapped in the scrotal tissues, this results in scrotal swelling. If the capillaries (tiny blood vessels) leak fluid into the surrounding tissue the area will start to swell. This could be due to capillary damage or increased pressure.
Leaking capillaries will cause the kidneys to accumulate higher than normal quantities of sodium (salt) and water in order to compensate for the capillary fluid loss. This results in more blood circulating in the body, which in turn causes even more capillary leakage into the surrounding tissue, which produces additional swelling – a vicious cycle
The most prominent cause of scrotal edema include:
- Physically inactivity- most common to those who do not excesses or walk very little.
- Standing or sitting for long.
- Surgery especially vasectomy
- Burns, this due to the fact that the skin react to a burn by retaining fluid, this would result in a scrotal swelling.
- Allergies, some foods and insect bites may cause edema in susceptible people.
The symptoms of scrotal edema vary depending on the underlying cause. Generally the symptoms would include:
- Scrotal swelling
- Shiny stretched skin
- Itchiness
- Enlarged scrotum, and abdominal size- ascites
The treatment option for the edema also vary. In order to treat scrotal edema, you doctor has to diagnose the cause of the edema. The Different treatment that would help reduce the chances of edema include:
- Cut down salt consumption
- Do regular exercise, to lose weight
- Raise the legs several times per day to improve circulation
- Wear supporting stockings
- Do not to sit/stand still for too long
- Get up and walk about regularly when travelling by car, train, boat or plane
- Avoid extremes of temperature, such as hot baths, showers, and saunas. Dress warmly if it is cold
- Massage – if the affected area is stroked firmly in the direction of the heart it may help move the fluid. It is important that the hand movements do not cause pain. A qualified masseuse or physical therapist will know how to do this more effectively.
2. Testicular cancer
Testicular cancer is a cancer that originates in one or both testicles, or testes. Testicular cancer often begins with changes in the germ cells, which are the cells in the testicles that produce sperm. Testicular cancer is sometimes referred to as a germ cell tumor.
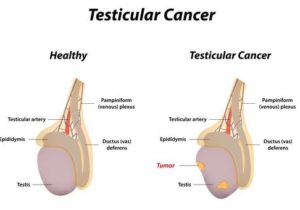
The two main types of testicular cancer are seminomas and nonseminomas. Seminomas are testicular cancers that grow slowly. They’re usually confined to the testes, but the lymph nodes may also be involved. Nonseminomas are the more common form of testicular cancer. This type is faster growing and may spread to other parts of the body.
The most common symptom of testicular cancer would include:
- testicular pain or discomfort
- swelling of the testicle
- lower abdominal or back pain
- enlargement of breast tissue
You need to see your doctor immediately you notice the above symptoms, there different treatment categories for testicular cancer, depending on the stage of your cancer, you may be treated with one or more options,
- Surgery is used to remove one or both testicles and some surrounding lymph nodes to both stage and treat the cancer.
- Radiation therapy uses high-energy rays to kill cancer cells. It may be administered externally or internally. External radiation uses a machine that aims the radiation at the cancerous area. Internal radiation involves the use of radioactive seeds or wires placed into the affected area. This form is often successful in treating seminomas.
- Chemotherapy uses drugs to kill cancer cells. It’s a systemic treatment, which means it can kill cancer cells that have traveled to other parts of the body. When it’s taken orally or through the veins, it can travel through the bloodstream to kill cancer cells.
3. Scrotal swelling after hernia surgery
A hernia occurs when an organ pushes through an opening in the muscle or tissue that holds it in place. For example, the intestines may break through a weakened area in the abdominal wall.
Hernias are most common in the abdomen, but they can also appear in the upper thigh, belly button, and groin areas. Most hernias are not immediately life threatening, but they don’t go away on their own and can require surgery to prevent potentially dangerous complications. One may experience scrotal swelling after such medical procedures.
4. Infection
Scrotal swelling as a result of a sexually transmitted diseases could be as a result of, epididymitis(inflammation of the tube that carries sperm from the testicles to the penis) caused by STI such as chlamydia or gonorrhea. These STDs can cause a range of other symptoms beside swollen testicles. Orchitis (inflammation of one or both of the testicles) can also be caused by several types of bacteria and some viruses (including the virus that causes mumps).
You should see you doctor to advice on the best treatment.
5. Vasectomy
After having a vasectomy, you may feel a dull ache and mild pain in your scrotum and groin as the anesthesia wears off. Most men experience scrotal swelling and minor pain at the site of the operation for two to three days after the procedure, although the exact length of time will vary from person to person. This pain is often described as an ache or feeling of tenderness. Many men report resuming light activity within a day or so, while others need to wait a little longer.
Doctors who perform no-scalpel vasectomies often claim lower levels of pain due to reduced trauma to the scrotum. An over the counter painkiller might work to reduce the pain, but if the pain does not stop, you need to call your doctor.
6. Jock itch
Jock itch, also referred to as ringworm of the groin, tinea cruris, or (in some circles) crotch rot, is caused by a fungus called Trichophyton rubrum. This particular type of fungus grows in warm and moist areas in the groin, inner thighs and buttocks. It occurs more commonly among adult men and adolescent boys, and (most commonly) athletes. It results from friction with the use of tight clothes combined with prolonged exposure to excessive sweating in the groin area.
Jock itch appears as a rash, redness, and scaling of the inguinal folds (front crotch zone) and may extend into the crack region. The rash usually has well defined edges. Jock itch can be contagious and spread by direct skin to skin contact and poor hygiene.
It is extremely common and very easy to treat. There exist a wide range of antifungal cream, powders and sprays available over the counter. It good you see a doctor who would be able to prescribe a stronger medication if the itch persists. It’s also important to keep your nether regions super clean and dry during your recovery. This means showering and changing underwear frequently.
7. Scrotal swelling STI
Scrotal swelling as a result of a sexually transmitted diseases could be as a result of, epididymitis(inflammation of the tube that carries sperm from the testicles to the penis) caused by STI such as chlamydia or gonorrhea. These STDs can cause a range of other symptoms beside swollen testicles. Orchitis (inflammation of one or both of the testicles) can also be caused by several types of bacteria and some viruses (including the virus that causes mumps).
Swollen testicles, or a sensation of a fullness in the testicle, can also be caused by an inguinal hernia. Inguinal hernias occur when part of the intestine becomes displaced, slipping through the inguinal canal into the testis. This creates a noticeable bulge in the testicular sac, swelling, and sometimes pain as the intestinal loop is confined in such a small space.
Severe testicle pain requires immediate medical care. You should seek immediate care if:
- Your testicular swelling is accompanied by severe or sudden pain, nausea, or vomiting
- You feel a lump in the scrotum
- Your swelling is accompanied by fever
- Your scrotum is tender to the touch, is red, or feels warm
- You have been in recent contact with someone who has mumps (virus that can cause orchitis)
8. Varicocele
These are soft lumps that develop gradually above the testicles and mostly on the left side of the scrotum. Sometimes described as feeling like a “bad of warms”. The exact cause of varicoceles is not clear but it is widely thought that they occur as the result of abnormalities in the veins in the testicles leading to a build-up of excess blood in the veins, which makes them swell.
The size of varicoceles can vary. Some may only be noticeable when you touch them. Others can be larger and seen easily. The side of the scrotum that contains the varicoceles may hang slightly lower than the other side. Besides a lump, varicoceles do not usually cause any other symptoms, although some men who have them experience a heavy feeling or aching pain in their scrotum or groin. They do not cause cancer and are not life threatening, but are simply an anatomic consequence of being human.
Varicoceles can be very uncomfortable and cause scrotal swelling which could be painful. This pain is generally mild and to moderate, occurring with long periods of sitting, standing, or activity and is relieved by lying down. The pain is dull, congestive. It is not associated with urination issues or erectile dysfunction; however, it is associated with male infertility. Lastly, when large, a varicocele can cause a clumpy “bag of worms” feel in the scrotum and can be bothersome.
9. Mumps
Mumps is a contagious disease caused by a virus that passes from one person to another through saliva, nasal secretions, and close personal contact. Pain and scrotal swelling affects one in four males who get mumps after puberty. The swelling is usually sudden and affects only one testicle. The testicle may also feel warm and tender.
There is no treatment for mumps itself, but age-appropriate painkillers, such as paracetamol or ibuprofen may help relieve some of the symptoms. A cold compress such as a moist flannel may help relieve some of the pain from the swollen glands. Applying cold or warm compresses to your testicle and wearing supportive underwear may also reduce any pain.
10. Epididymitis
Epididymitis is an inflammation of the epididymis. The epididymis is a tube located at the back of the testicles that stores and carries sperm. When this tube becomes swollen, it can cause pain and scrotal swelling.
Epididymitis may begin with only a few mild symptoms. When it’s left untreated, however, the symptoms tend to get worse. Most common symptoms include:
- a low-grade fever
- pain in the pelvic area
- pressure in the testicles
- pain and tenderness in the testicles
- redness and warmth in the scrotum
- enlarged lymph nodes in the groin
- pain during sexual intercourse and ejaculation
- pain during urination or bowel movements
- urgent and frequent urination
- abnormal discharge
- blood in the semen
Treatment for epididymitis involves treating the underlying infection and easing symptoms.
Common treatments include:
- antibiotics
- pain medication
- anti-inflammatory medication
- bed rest
- elevating the scrotum
- applying cold packs to the scrotum
- wearing an athletic cup for support
- avoiding lifting heavy objects
- abstaining from sexual intercourse
11. Hydrocele
A hydrocele is a sac filled with fluid that forms around a testicle. Hydroceles are most common in babies. According to the Official Foundation of the American Urological Association, nearly 10 percent of males are born with a hydrocele. However, they can affect males of any age.
Hydroceles generally don’t pose any threat to the testicles. They’re usually painless and disappear without treatment. However, if you have scrotal swelling, see your doctor to rule out other causes such as testicular cancer.
12. Trauma
Despite the vulnerable position of the testicles, testicular trauma is relatively uncommon. The mobility of the scrotum may be one reason severe injury is rare. Given the importance of preserving fertility, traumatic injuries of the testicle deserve careful attention. So if this happens one my experience scrotal swelling. It is good you see to doctor in cases of such emergencies.
Swollen left testicle with pain
Swollen left testicle can arise from several different causes, some of which would be as a result of a medical emergency. Scrotal swelling may be perceived when there is localized enlargement of the scrotum or enlargement of the testicles. Swollen left testicle may or may not be accompanied with pain and other symptoms.
Swollen left scrotum can result from testicular torsion, a medical emergency. This is a condition in which the testicle twist inside the scrotum, causing an interruption of the blood supply to the testicle. You need to see your doctor as soon as this happen. The interruption of blood supply could cause tissue death of the affected testicle. Inflammation or epididymis of the left testicle could also be the cause of swollen testicle.
Other causes include anatomical abnormalities, infections, hernia, and tumors. A hydrocele is a benign buildup of fluid around a testicle that can appear as testicular or scrotal swelling. A varicocele is the enlargement of veins within the scrotum and does not involve the testicles themselves. Testicular cancer is an uncommon cause of swelling in the testicle. When congestive heart failure causes fluid buildup in the lower extremities, it can be so severe as to cause scrotal swelling, although the testicles themselves are not affected.
Swollen testicle with pain
Painful scrotal swelling can start suddenly or gradually. Painful swelling is less common than painless swelling, but is usually more serious, especially if the enlargement and the inflammation is severe and sudden. You need to see your general practitioner as soon as you notice the symptom. Your doctor will advise on the best cause of medication. The most common causes of a painful swollen testicle include:
Testicular torsion
This condition is caused when a testicle twists on its cord. A twisted cord can cut off a testicle’s blood supply and may require emergency surgery—ideally within six hours of the onset of symptoms to save the testicle. Pain is sudden and severe.
Epididymitis and orchitis
These are infections that can be caused by bacteria or viruses. Pain is less severe and more gradual than with torsion. Viral infection of the testicle (orchitis) can be seen in young boys who contract mumps. Epididymitis, marked by a feeling of heaviness, tenderness, and swelling in the scrotum, is usually a bacterial infection of the ducts near the testicle that are important for the storage and development of sperm. Several sexually transmitted diseases, including chlamydia and gonorrhea, can cause epididymitis.
Zipper entrapment
If part of the scrotum, foreskin, or penis gets caught in a zipper, it can cause immediate, agonizing pain. Emergency room doctors commonly treat both pain and injury while freeing the entrapped tissue.
Other causes. Less common causes of painful swelling include other injuries, allergic reactions, and insect bites. Schönlein-Henoch purpura is a condition that may cause painful scrotal swelling in young boys along with rash, joint pain, stomach pain, and blood in the urine; its cause is unknown.
Swollen testicle treatment
Treatment options for scrotal swelling mostly depend on the cause. If an infection caused the swelling, your doctor will prescribe antibiotics to fight the infection. If oral antibiotics do not work, you may have to receive intramuscular antibiotics
Treatment of an underlying medical condition that is linked to your symptoms is important in your recovery. Your doctor can prescribe medications to help you manage your pain and may recommend a supportive garment to ease pain and swelling. Surgery may be necessary to correct the condition if the underlying cause is varicocele, hernia, or hydrococele.
At times the swollen testicle maybe as a result of Testicular cancer, in that case several treatment options are applicable, the treatment will depend on the severity of the cancer. Whether the cancer has spread, and how long it went undetected will determine your treatment, which normally consists of the following:
- chemotherapy
- radiation therapy
- surgery, which involves removing cancerous tissue and cancerous tumors from the scrotal sac )
Scrotal swelling home treatment
other than medical treatment from professional doctor, you treat enlarged scrotum with various home remedies. These include:
- using ice on the scrotum to relieve swelling, normally within the first 24 hours of noticing the swelling
- taking an over-the-counter pain reliever
- wearing athletic support
- using a sitz, or shallow bath to reduce swelling
- Avoiding strenuous activities that calls for lot of body movements.
Further references
- Testicular lumps and swelling:http://www.nhs.uk/Conditions/Testicular-lumps-benign/Pages/Causes.aspx
- Scrotal swelling: http://www.healthline.com/symptom/swelling-of-scrotum
- Scrotal swelling: https://medlineplus.gov/ency/article/003161.htm
- Scrotal swelling: https://www.merckmanuals.com/home/kidney-and-urinary-tract- disorders/symptoms-of-kidney-and-urinary-tract-disorders/scrotal-swelling
- Testicle Pain: http://www.mayoclinic.org/symptoms/testicle-pain/basics/causes/sym-20050942
- Testicular swelling:http://www.medicinenet.com/swollen_testicles/symptoms.htm



